The power transmission industry plays a critical role in the Power sector ecosystem. As an equity investor, understanding the key metrics of this industry is vital for making informed investment decisions. In this blog, we will delve into the basics, the two important metrics of this industry, the Indian landscape, challenges and opportunities. (Featured image credits: https://www.sterlitepower.com/)
Hi, This is Venkatesh. I write on Personal Finance, Stock Investing, Productivity and Time Management. You will be interested to read more about me and the purpose of my website.
If you are interested in these topics do subscribe to my blogs. You would maximum receive 4 to 5 emails a month.
Power Transmission - The Basics
What Power Transmission does?
- Transmission industry serves as a crucial link connecting power generation and power distribution.
- The power transmission infrastructure transfer electricity from power-generating companies to substations located near consumers.
- This is accomplished through a network of high-voltage transmission lines.
The transmission lines we observe from our train windows or cars are not just passive infrastructure; they serve as active “electricity highways,” transmitting power every second.
Power Transmission Infrastructure
- The power transmission infrastructure consists of transmission lines, substations, switching stations, transformers, and distribution lines.
- Within the transmission network, different voltage levels are employed to cater to specific transmission requirements.
- This includes the use of 765 kV, 400 kV, and 220 kV AC networks, with the highest voltage level reaching 800 kV in the case of HVDC (High-Voltage Direct Current) transmission.
The below image would give a better clarity of what is said above. You could see the power from Power Generation station going through step-up transformer and then through the Transmission lines network. At the receiving end there is a step-down transformer in the sub station.
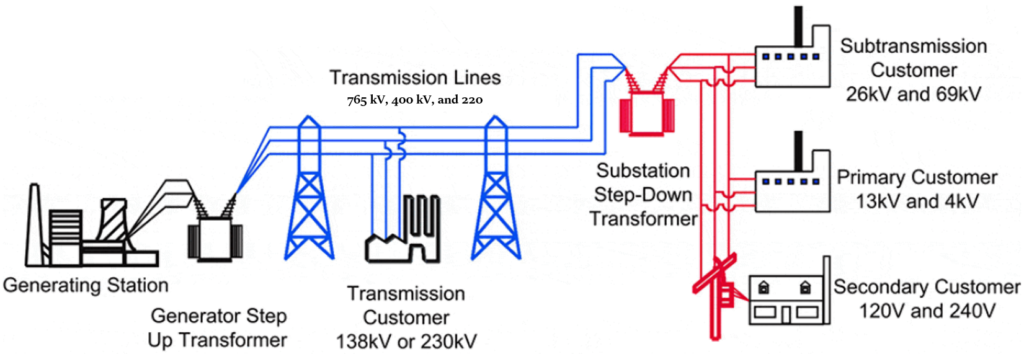
Image reference: https://electrical-engineering-portal.com/substation-basics
Key Metrics
Each industry in the Power Sector has its own key metrics. In case of Power Generation we saw that it was Installed Capacity. Similar metrics exits for the Transmission industry as well.
We saw that the power transmission has 3 main activities, (1) Steps-up the generated power, (2) Transmit the power over long distances and (3) Step-down the power to fit the consumer requirements.
In line with these activities there are two important metrics in the Transmission industry.
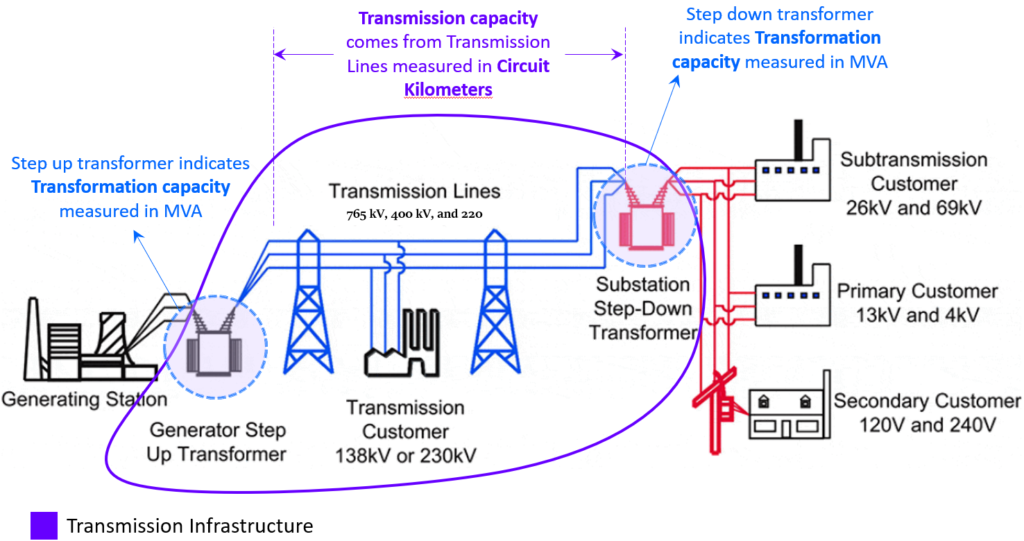
- One metric measures the capacity of step-up and step-down of the transformers. This is the transformation capacity measured in MVA (Mega Volt Amps)
- Another metric measure the distance over which the electricity is transmitted. This is the transmission capacity measured in Circuit Kilometers
Transmission Capacity (Circuit Kilometers)
- Circuit kilometres is the total length of the conductors used in the transmission line network.
- It is the cumulative distance of the conductors in the transmission system.
- The calculation of Circuit kilometres take into account the length of all the transmission line conductors, including both the supply (outgoing) and return (incoming) lines.
This is an important metric used to measure the scale and extent of the transmission network, indicating the total length of conductors required to transmit electricity from power generation sources to substations and ultimately to consumers.
Transformation Capacity (MVA)
- Power generation occurs at various voltage levels, which may not be optimal for efficient transmission or consumption by end-users.
- Therefore, it becomes necessary to adjust the voltages to meet consumer requirements.
- Transformers play a crucial role in stepping up or stepping down the voltage levels.
- The transformation capacity denotes the total capacity of transformers installed in the transmission system, enabling them to handle these voltage transformations and ensure smooth power flow.
Getting a bit Technical!
The level of detail provided in this heading may not be of interest to an investor. However, remember that you will be reading annual report of these companies, where you will come across these terms. A bit of Technical background helps you with better understanding. Alternatively, you can choose to skip this section.
Transmission and Transformation Capacity
At a high level the Power transmission mainly focus two activities, (1) Step-up/down of the power and (2) Transmission of the power. The images depict, where the Transmission capacity and Transformation fits in the bigger Power Transmission industry.
Difference between kilometre and circuit kilometer
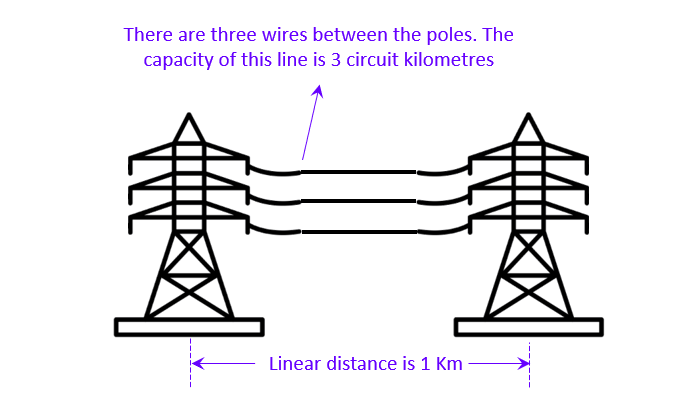
- Kilometer simply represents the linear distance between two points on a transmission line, indicating the physical length of the line.
- Circuit kilometers, on the other hand, take into account the total length of the conductors used in the transmission line network, considering all the wires carried by the transmission poles.
To illustrate this with better clarity, let’s consider a simplified image:
- Imagine two transmission poles with a distance of 1 kilometer between them (Note that in reality, a few hundred meters is only feasible between poles, but for the purpose of this simplified explanation, let’s assume 1 kilometer).
- Now, imagine that there are three wires carried by these poles.
- In this scenario, the linear distance between the poles is 1 kilometer, but the measurement of the transmission capacity would be 3 circuit kilometers, considering the total length of the conductors in the transmission line.
Industry Challenges and Trends
The power transmission industry faces several challenges, including:
Investment
Constructing new transmission lines, substations, and equipment requires significant investments. Like other sectors in the power industry, substantial financial resources are needed to support the development and expansion of power transmission infrastructure.
Long TImelines
Power transmission projects often require acquiring vast stretches of land for constructing the transmission network. The availability of suitable land and potential issues in land acquisition can lead to project delays. Moreover, geographical constraints can further complicate the installation process, adding to the project timelines.
Geographical Constraints
Challenging terrains such as difficult terrains, mountainous regions, dense forests, rivers or natural obstacles pose hurdles in laying transmission lines and constructing infrastructure. Overcoming these geographical constraints requires specialized machines, skills and infrastructure. All these contribute to project timelines and costs.
Grid Integration of Renewable Energy
Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the power grid presents challenges due to their intermittent and variable nature. The transmission infrastructure must be capable of handling the fluctuations in power output from renewable sources while ensuring grid stability and balancing supply and demand.
Grid Security and Cybersecurity
As power transmission systems become increasingly digitized and automated, ensuring grid security and protecting against cybersecurity threats becomes crucial. Safeguarding transmission infrastructure from physical and cyber threats is necessary to maintain the reliability, resilience, and integrity of the power grid.
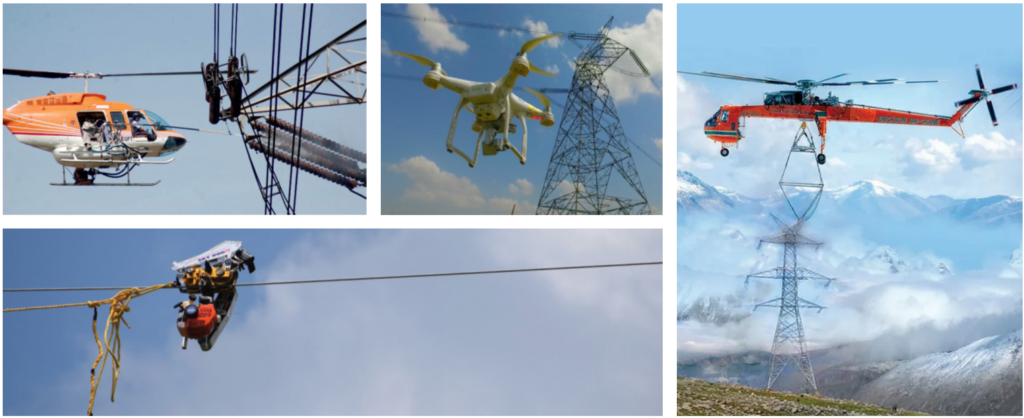
Technology is helping to overcome a few of the challenges. A few areas are:
- Use of Helicopter stringing
- Heli-crane based tower erections in tough terrains
- Use of Robots for safe and efficient optical ground wire stringing
- Drones are used for surveillance and to ensure grid security.

Indian Scenario
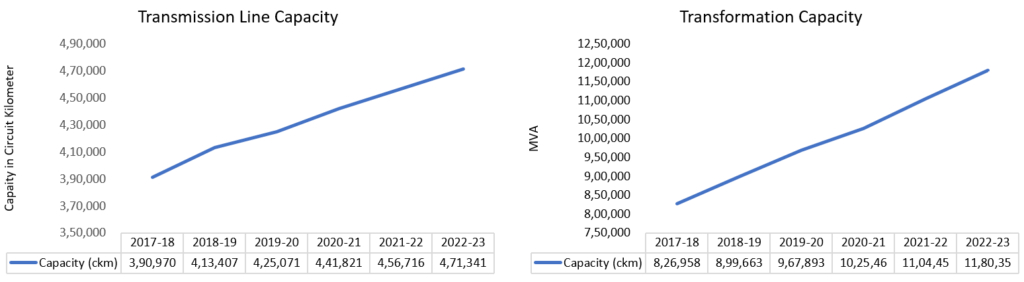
Unlike power generation, power transmission is a licensed activity. In India, a comprehensive network of transmission lines has been developed over the years to effectively evacuate power generated by diverse power stations and distribute it to consumers. This is very much reflected in the growth of the Transmission and Transformation capacities.
Transmission can be:
- Inter state transmission: The power transmission happens between more than one state in India
- Intra state transmission: The power transmission happens within a state
- Cross border inter connections: The power transmission is beyond Indian geographies. Some power transmission companies have business with few neighbours like Nepal, Bhutan etc.
Notable Companies
There are many transmission companies. Some could be held by the state governments. Below is a few listed companies in this industry.
- Power Grid Corporation of India Limited – This is a state-owned company and the central transmission utility of India.
- Adani Transmission Limited
- Sterlite Power Transmission Limited
- Tata Power Transmission – This is a subsidiary of Tata Power
- Essel Infraprojects Limited
We will discuss more of the individual companies and their capacities in the future blog.
What makes Power Transmission attractive for Investors
A once boring industry for investors becomes of interest. The reason behind is two fold, (1) General growth in the power sector in the coming years needing more power generation and transmission, (2) Growth in the renewable mode of power generation.
Let us deep dive a bit more.
- A few years ago, the power transmission sector was perceived as having marginal growth and limited investor interest.
- Once a power transmission line was commissioned, it was considered a long-term fixture without the need for further development.
- Growth opportunities only arose when new power generation capacities were established in new locations, necessitating the construction of new transmission lines or upgrades to existing capacities.
- However, a significant change occurred when renewable energy, such as solar and wind, became more cost-competitive compared to conventional power sources.
- Unlike conventional energy, solar and wind energy could be harnessed from numerous locations across the country.
- This led to a demand for new transmission lines to evacuate this renewable power.
- Suddenly, a sector that previously experienced minimal year-on-year growth found itself at the forefront of an unprecedented opportunity.
- Thus a greater capacity will be mandated by the power transmission sector to transmit power from the renewable-rich regions to the rest of the nation.
Reference: Adani Transmission 2022 Annual Report
Conclusion
India continues to focus on expanding its power infrastructure and integrating renewable energy sources, the Power Transmission Industry will play a pivotal role in facilitating the transmission of clean and sustainable power. The Indian Power Transmission Industry offers promising opportunities for equity investors seeking exposure to the energy sector.
Hope you found this blog useful. Do share my blogs with your friends, peers and fellow investors.

