In this blog, we will discuss the importance of sector and industry analysis. (Featured image credits: Image by Elf-Moondance from Pixabay)
Warren Buffett, in his 2007 letter to his shareholders, classified businesses into three categories: great, good, and gruesome. The most straightforward option for an investor is to invest in great and good businesses (at a reasonable valuation) and avoid gruesome businesses. Saying this is simple, but putting it into action is challenging.
So, how does an investor find out where their company fits in these three categories? To determine the answer to this question, understanding the sector and the industry to which the business belongs plays a vital role. (In this blog, I will use the words ‘company’ and ‘business’ interchangeably.)
Hi, This is Venkatesh. I write on Personal Finance, Stock Investing, Productivity and Time Management. You will be interested to read more about me and the purpose of my website.
If you are interested in these topics do subscribe to my blogs. You would maximum receive 4 to 5 emails a month. Do check my Blog Index for all my blogs.
Difference between a Sector and an Industry
It is often mistaken
Do the words ‘sector’ and ‘industry’ appear synonymous? If you think they are, the answer is ‘No’. The investing community uses both these terms interchangeably. But there is a distinct difference between the two. As you read this blog you will understand:
- The differences between a Sector and an Industry
- Scope of Sector and Industry Analysis
- The importance of this analysis for an Investor.
The Big Picture
To understand the difference, it is necessary to examine the positioning within a country’s economy.
- A country’s economy comprises distinct sectors, each characterized by its unique attributes and lacking commonality.
- Within each sector, there are numerous industries that share common business activities, ranging from a few to many.
- Each industry, in turn, encompasses a multitude of companies or businesses that share similarities in terms of inputs/raw materials, technology, manufacturing processes, operating models, and end products or services.
While the sector represents a broad classification, the industry provides a more specific categorization. The following mind map visually represents this concept.
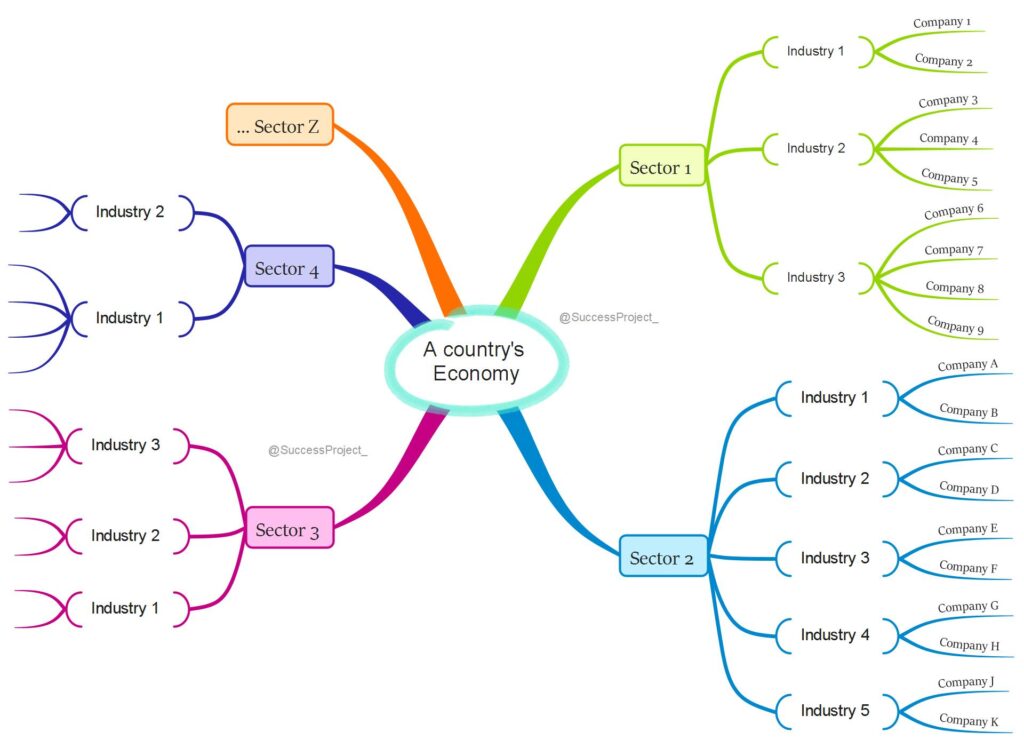
From the perspective of an investor, it becomes evident that:
- The company in which you intend to invest belongs to an industry.
- This industry represents a segment within a sector.
- Furthermore, this sector forms an integral part of the country’s economy.
By now, it should be clear to you that sector and industry are not synonymous.
Practical Walkthrough
Let us discuss the idea with an example.
Sector
The Indian economy encompasses numerous sectors, including well-known ones such as Financials, Healthcare, Telecom, Construction, Chemicals, Metals, Mining, and more.
Industry
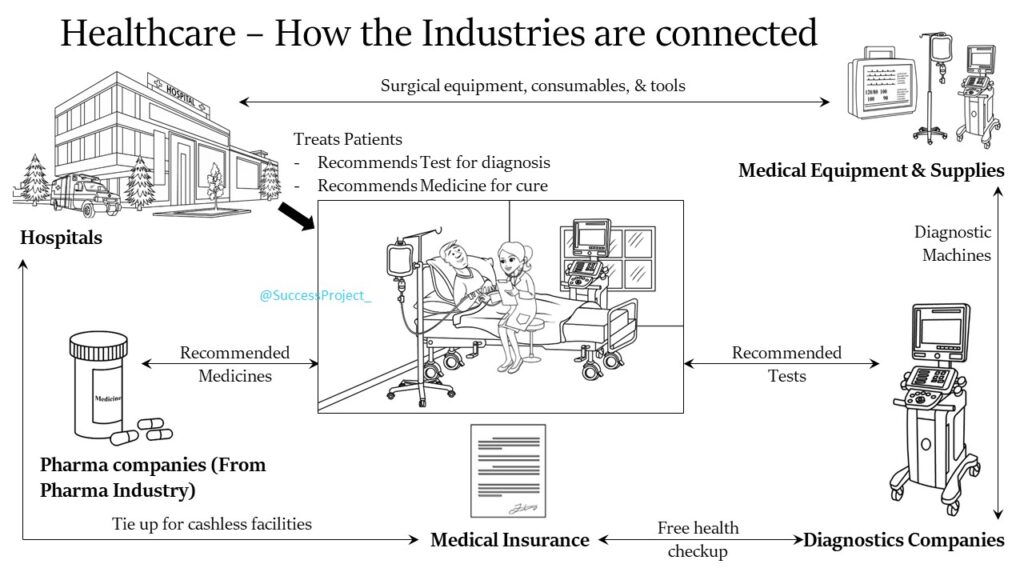
We will focus solely on the Healthcare sector, which comprises several industries, namely (1) Hospitals, (2) The Pharma industry, (3) The Diagnostics industry, and (4) Medical device manufacturers. It is evident that there exists a connection among these individual industries. To illustrate this, consider the following scenario:
- A patient visits a hospital for consultation.
- The doctor recommends specific tests for diagnosis.
- The patient then proceeds to a Diagnostic lab (which operates within the diagnostic industry) to undergo the tests.
- Based on the test results, the doctor prescribes suitable medicines. These medicines are manufactured by the pharma industry.
The interdependence within this ecosystem is visualized in the image below.
Likewise, other sectors such as Financials, metals, mining, and so on, consist of multiple industries.
Company
Now, let’s explore the various companies operating in different industries of the healthcare sector:
- In the Hospital industry, there are numerous private hospitals and listed companies such as Apollo, Narayana Hrudayala, and more.
- The Pharma Industry consists of several listed companies engaged in drug manufacturing, including names like Sun Pharma, Divi’s Lab, Cipla, and others.
- The Diagnostic industry comprises a substantial number of private labs and listed companies such as Thyrocare, Dr Lalpath Labs, Metropolis, Vijaya Diagnostics, Krisnaa Diagnostics, and more.
The below mind map visually represents the discussion mentioned above.
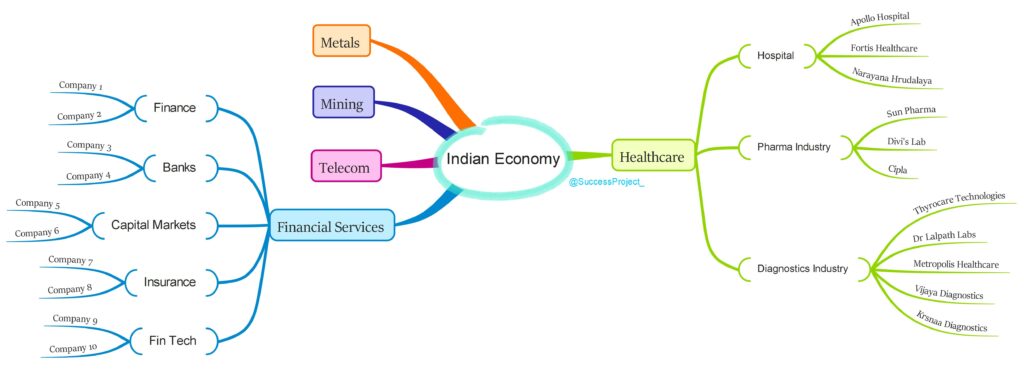
This illustrates the interrelation between a sector, industry, and the constituent companies involved.
Where can Investors find this Information?
There are two primary sources through which investors can obtain details about sectors, industries, and the companies within them.
Moneycontrol
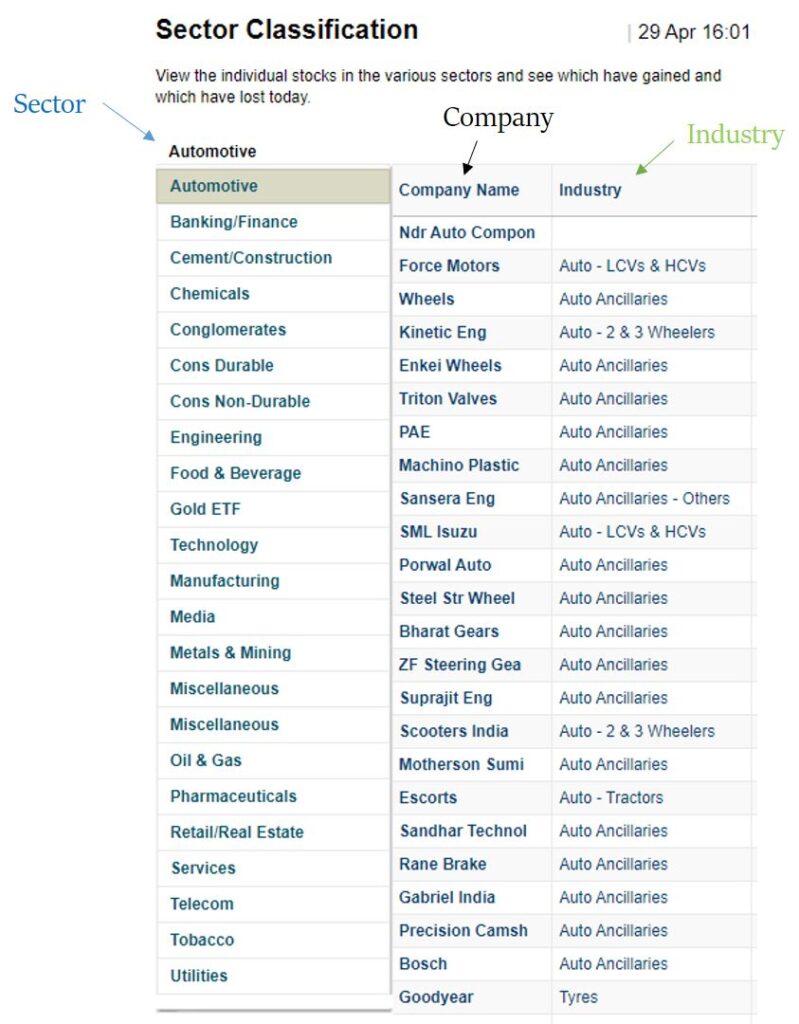
To understand the various sectors and industries in the Indian market, refer to this page on MoneyControl. The image below depicts the information, where the first column represents the sector, the third column indicates the industry, and the second column specifies the companies within each industry.
BSE Website
The BSE website offers a helpful PDF that facilitates comprehension of the diverse sector and industry classifications of listed companies in India. This classification system provides insights into sub-segments within the industry, offering a more detailed perspective.
However, it is essential to note that various portfolio websites and screens may utilize slightly different terminologies and sub-industry classifications.
Disclaimer
The above information aims to assist investors in comprehending the following aspects:
- The distinction between sector and industry.
- The positioning of a country’s economy and an analyzed company within this broader context.
It is important to note that this perspective may differ from an academic definition, which typically categorizes a nation’s economy into four high-level sectors: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary. However, please refrain from using the provided content for academic purposes as it may not align with traditional academic definitions.
Scope of Sector and Industry Analysis
Having comprehended the distinction between a sector and an industry, let us now delve into the scope of these analyses.
Sector Analysis
- Sector analysis is an assessment of the economic condition, financial condition and prospects of a given sector in the economy. (Reference: Sector Analysis, Investopedia)
- Sector analysis helps to understand the current condition and prospects of a given sector of the economy.
- This is more focused on economic growth, sector cycles, government policies and incentives, and interest rate impact.
Sector analysis gives an investor a view of the business activities in a sector.
Industry Analysis
Industry analysis plays a crucial role in providing insights into the position of the company of interest compared to other industry players.
It focuses on various aspects, including the overall industry size, functioning, companies within the industry (with emphasis on market position, competition, and pricing power), supply-demand dynamics, growth drivers, technology disruptions, regulatory environment, risks, and the industry’s life cycle.
For an investor, industry analysis offers the following benefits:
- Identifying favourable industries within a sector.
- Gaining an understanding of the performance of companies operating in a specific industry.
My next blog delves into industry analysis in detail, covering its various aspects comprehensively.
Which is Important? Sector or Industry Analysis?
Now, a pertinent question arises: which of these two analyses holds more significance for an investor?
It is important to note that sector and industry analyses are interdependent and cannot be considered in isolation. An investor must assess a company from both sector and industry perspectives. This is because:
- Sector analysis helps in avoiding sectors that may not be suitable for long-term investing.
- Different sectors of the economy perform differently at various stages of the business cycle. Therefore, sector analysis aids in identifying profitable investment opportunities based on the prevailing economic conditions.
- Within a favorable sector, not every industry is equally attractive. Despite having related or common business activities, industries exhibit differences. Hence, industry analysis helps in pinpointing the favorable industries within a chosen sector.
- Numerous companies exist within an industry, and while they may share similarities, not all companies are suitable for investment. Factors such as market share, pricing power, and unique product differentiation vary among companies.
- Therefore, industry analysis assists in identifying the most suitable company within a sector, which forms the crux of the analysis.
When making long-term investments, it is crucial to comprehend both the sector and industry dynamics to which the company belongs.
Practical Example from Auto Sector
Let’s delve into this idea further with a practical example from the Auto sector.
- When considering the Auto sector, its cyclic nature is a key insight that comes to mind, which may lead an investor to avoid this sector.
- However, the understanding changes when we extend the analysis to the industry level. The Auto sector comprises industries such as OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturers or Automakers), auto ancillary, and tyre manufacturers (although there are more industries within this sector, we will focus on these three for illustration purposes).
- At the industry level, the level of cyclicality varies. Auto ancillary and tyre industries demonstrate relatively lower cyclicality compared to OEM.
- The reason behind this lies in the supply chain dynamics. These industries supply their products not only to OEMs but also to retail customers. For instance, a tyre manufacturer supplies to both car manufacturers and retail customers, with car owners replacing their old tyres through workshops.
- During a slowdown in the Auto sector, OEMs experience a major setback, whereas the impact on the tyre industry is relatively lesser. Although there may be reduced sales to OEMs, stable sales in the retail market segment help mitigate the impact.
Similar business dynamics apply to Auto ancillary companies as well. Hence, even within the Auto sector, the Auto ancillary and tyre manufacturers demonstrate less impact compared to the OEMs.
In Summary...
- If you solely rely on sector analysis, you would likely completely avoid the auto sector.
- However, by conducting both sector and industry analysis, you can uncover auto ancillary and tyre manufacturers that exhibit lower cyclicality. By delving into detailed industry analysis, there is a possibility of identifying a company with secular growth.
- This can be attributed to the company’s diverse customer base, supplying to OEMs, retail customers, and even foreign OEMs. This mix of market segments enables the company to mitigate the cyclical nature of the sector.
Therefore, through industry analysis, you have the potential to identify a company with secular growth that would have been overlooked with only sector analysis. Hence, for investors, it is crucial to consider both sector and industry analysis.
Conclusion
Sector and industry analysis play indispensable roles in investment decision-making. While sector analysis helps investors identify favorable sectors and avoid potentially volatile ones, industry analysis delves deeper into specific industries, uncovering opportunities and risks within them. Understanding the interplay between sectors and industries provides valuable insights into a company’s positioning, competition, market dynamics, and growth potential. By considering both sector and industry analysis, investors can make informed decisions, identifying companies with secular growth and mitigating the cyclicality inherent in certain sectors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of sector and industry dynamics is essential for successful investment strategies.
The next blogs will cover topics related to Industry analysis on:


Good one. Thanks for your effort to educate the common people
You are welcome. Thanks for your words.
Pingback: How to Do Industry Analysis - Venkatesh