This blog, will focus on the Diagnostics Market Segment. In the last blog, we saw a high-level overview of the Indian Diagnostics Industry. (Featured image credits: https://www.drmaidhospital.in/diagnostic-services-in-multispecialty-hospital/)
Diagnostics is an important part of the healthcare sector. It helps in the diagnosis of the health condition of a patient. This is the first and most important step in disease management. Without this accurate identification, it is not possible to provide the correct treatment.
The diagnostic market can be segmented in different ways. Below are 5 ways to segment it:
- Industry structure as Unorganized Vs Organized
- Geographical demographics as Urban Vs Rural
- Purpose/Stage of diagnosis as Prescriptive Diagnostics Vs Preventive / Wellness Diagnostics
- Services offered as Pathology Testing Services and Imaging Diagnostic Services
- Segmentation based on the Complexity of Tests
The first two ways of segmenting will be discussed in this blog, while the next blog is reserved for the next 3 segments.
Brief Background of this Blog Series
Diagnostics Industry was of interest to me since 2017. However, I could spend dedicated time only during 2021 to study this industry. The contents that you see in the coming blogs were mined from Annual Reports, Concalls, RHP, Management interviews and a few Twitter spaces by Mr Aditya Khemka and Dr Velumani.
Hi, This is Venkatesh. I write on Personal Finance, Stock Investing, Productivity and Time Management. You will be interested to read more about me and the purpose of my website.
If you are interested in these topics do subscribe to my blogs. You would maximum receive 4 to 5 emails a month.
You might also be interested to read these related articles:
Unorganized Vs. Organized
Unorganized Sector
The unorganized sector comprises of (1) Standalone diagnostic centers and (2) Hospital based labs. Historically, the diagnostic industry has been dominated by standalone diagnostic centers followed by hospital-based diagnostic centers.
Standalone diagnostics centers
- These are diagnostic centers with a single laboratory/center
- The absence of stringent regulations and the low-entry barriers have contributed to the establishment of several standalone diagnostic centers across the country
- Infact there is no accurate data on how many such diagnostic centres are there in the country
- Estimates however put it to 1 Lakhs centres (100K)
- Standalone centers usually carry out basic tests requiring minimal investment and physical space.
Hospital Based Centers
- Secondary and Tertiary Hospitals have their Pathology and Radiology on-site laboratories for the diagnosis of their patients (inpatient and outpatient).
- Hospitals that have physician practices generally require these physicians to refer tests to the hospital’s laboratory.
- Most hospitals have admitting privileges or other relationships with physicians located in the surrounding community and encourage such physicians to send patients for testing to the hospital’s laboratory. – This is another source of footfall to their labs.
- They however do not cover all the tests. This is around advanced tests where the equipment is expensive or volumes are low to make it economically viable. In such cases, they send the samples to advanced labs / Diagnostic chains
- Typically, hospitals with 100 to 150 beds or less prefer to outsource their tests rather than set up an in-house laboratory testing facility. (Reference: Vijaya Diagnostics 2022 Annual Report)
- Major hospital chains such as Apollo, HCG, Max, Fortis, etc., have their diagnostic arm, which caters to their requirements.
Organized Sector
Diagnostics Chains
- Diagnostic chains have emerged in recent years, offer pathology and imaging services and operate out of more than one center.
- Diagnostic chains benefit from economies of scale, standardized testing procedures, brand image and perception of quality
- They enjoy higher bargaining power with suppliers, which enables them to maintain lower operating costs when compared to their unorganized counterparts.
- Diagnostic chains adopt the hub-and-spoke model business model to extend their catchment area. (We will see how this happens in the future blogs)
- Due to the size of their operations, they can offer more complex as well as a greater range of tests than the unorganized sector.
- We saw in the last blog that this business relies heavily on trust and doctor referrals. Diagnostic chains enjoy a higher level of confidence among the doctors.
Diagnostic chains are further classified as,
Regional Diagnostics Chains
These centers are concentrated in a single city or state in India. The following are a few regional players who have a strong footprint in a particular region.
- North India: Quest Diagnostics, Core Diagnostics & Max labs
- West India: Suburban Diagnostics, & iGenetic Diagnostics
- East India: Suraksha Diagnostic
- South India: Medall Healthcare, Apollo Diagnostic and Vijaya Diagnostic Center.
Note: The above geographic grouping of the companies is not hard. As part of the expansion, companies do expand to other geographies.
Pan-India Diagnostics Chains
These have centers across the country. There are only a few large pan-India diagnostic chains in the country:
- Thyrocare Technologies
- Dr Lal Pathlabs
- Metropolis Healthcare
- Krsnaa Diagnostics and
- SRL Diagnostics (Part of Fortis Hospital)
Market Share of Different Segments
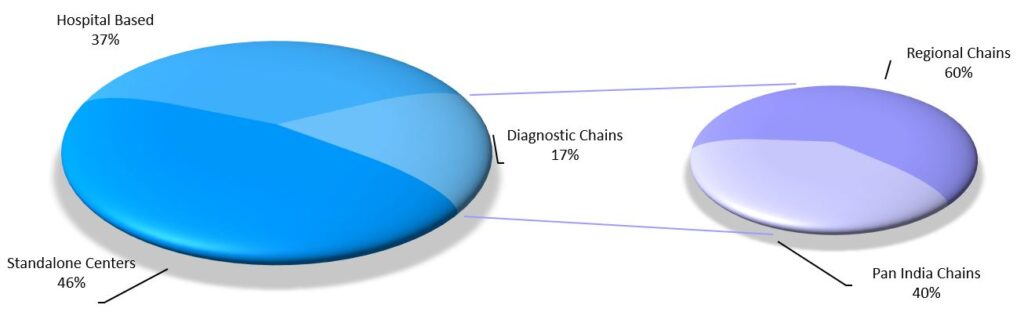
Source: Reference to CRISIL Research in Vijaya Diagnostics Annual Report 2022.
With close to 47% of the market share, the standalone centers have the highest market share.
Business Model Large and Small Labs:
Reference to the below two paragraphs: https://www.icra.in/rating/showmethodologyreport/?id=407&parentid=690
Large Labs
They have a professional and experienced managerial set up, fully automated equipment, follow standardised quality controls for material and lab processes and strive for regular up gradation of staff skill sets, thus commanding a good reputation, which would provide scope for attaining a larger scale through repeat customers. An organised chain would be able to establish a trusted perception in the market, which would support its funding requirements to expand both organically or inorganically. With a substantial scale of operations, these organised players benefit from operational efficiencies and are better positioned to make incremental investments in new labs and the latest technology, thereby reinforcing their brand reputation and increasing market share.
Small Labs
They are run in an unorganised manner by mostly family run businesses that lack the expertise and funding to procure the latest technology/equipment to provide specialised pathology or radiology services (although some of the equipment can also be taken on lease from third-parties which limits the amount of upfront investments), skill set to develop new tests and vision to grow in a pre-defined manner. Due to the lack of standardised systems in place and a limited test portfolio, these labs can lose customers to organised players and thus face scalability constraints.
Urban Vs. Rural Demand
Urban Demand
- Urban population live in Metros, Tier-I and Tier-II cities and enjoy modern facilities (at public and private hospitals, clinics, standalone centers and diagnostic chains)
- They have better access to healthcare delivery systems, including hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers.
- This is due to the greater participation of the private sector and the presence of large pool of doctors
- Disposable income: Higher and hence can afford (and have a higher demand for) more advanced healthcare services and facilities, including consuming a greater number of diagnostic tests.
- The prices of the same test are higher in urban when compared with rural
- Urban Population in India: 35.39%
Source: https://tradingeconomics.com/india/urban-population-percent-of-total-wb-data.html, 2022 Data
Rural Demand
These are largely primary health centers, government dispensaries and private dispensaries – generally have small-scale facilities and carry out basic tests where ticket sizes are usually lower than those charged in the urban centers.

Source: Vijaya Diagnostics Annual Report 2022.
To close…
In this blog, we discussed 2 ways of market segmentation. The next blog will cover the remaining 3 ways of market segmentation.
Hope you found this blog useful. Do share my blogs with your friends, peers and fellow investors.

