In this blog, we will discuss MNC Holding, (1) The different modes the parent company hold the Indian entity and (2) Direct Vs. fellow subsidiary. This understanding is essential to understand the various related party transactions that you will see in the next blog. (Featured image credits: https://www.duupdates.in/multinational-companies-india-mnc-india/amp/)
To better understand this blog, you need to read my four earlier blogs on MNC companies that cover:
- Overview of MNC Companies, their unique traits and premium valuation
- Royalty payments to overseas parents, investor concerns and views of the investment community
- Tools to Analyze Royalty – Part 1
- Tools to Analyze Royalty – Part 2
What is the information source?
All the information needed for this analysis comes from the Annual Report. In contrast to the Indian counterparts, the promoters i.e., The parent company, is referred to as “Holding Company”. Use this as the keyword and search the annual report. Review each occurrence for the context and you will get the needed information somewhere. We will see this approach with examples.
Hi, This is Venkatesh. I write on Personal Finance, Stock Investing, Productivity and Time Management. You will be interested to read more about me and the purpose of my website.
If you are interested in these topics do subscribe to my blogs. You would maximum receive 4 to 5 emails a month.
You might also be interested to read these related articles:
The overseas parent can hold the Indian listed entity through direct or indirect holding.
Direct Holding
The Indian listed entity is directly held by the overseas parent. To tell the other way, the Indian listed entity is the direct subsidiary of the overseas parent. Below is the pattern and example.
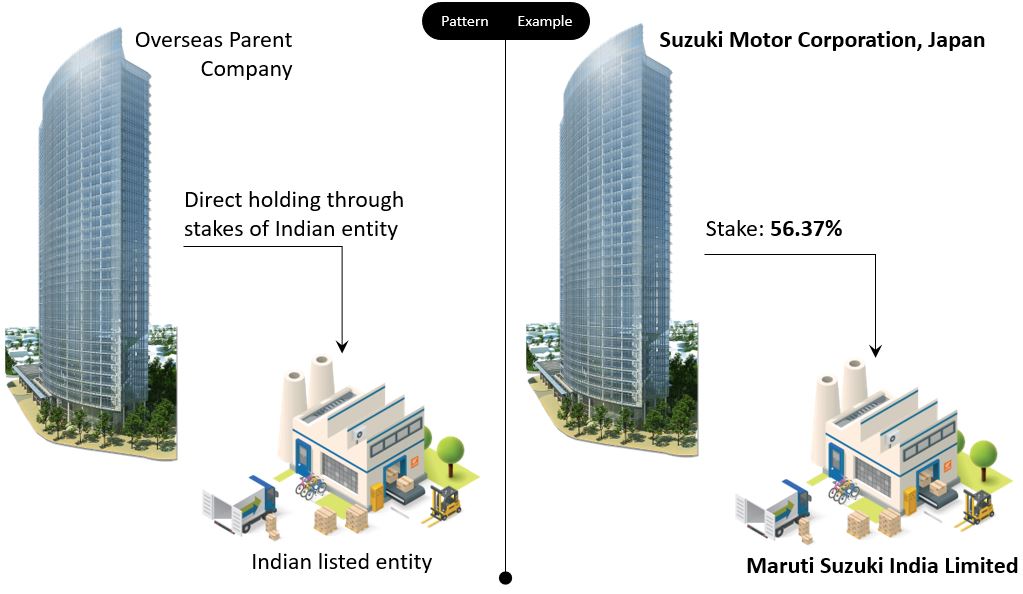
How to get this information?
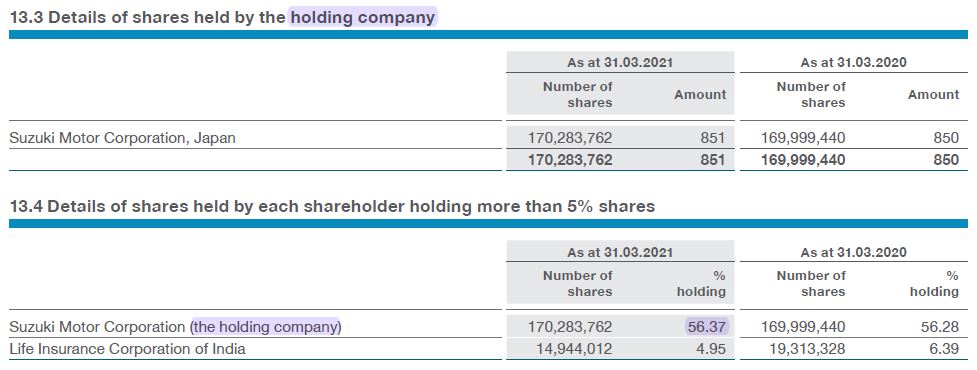
The information is taken from the Annual report. Search for the keyword “Holding Company” and you would get the needed details somewhere.
Indirect holding
The Indian listed entity is not directly held by the overseas parents. Rather the subsidiary/subsidiaries of the overseas parent hold the Indian listed entity. In this case, the Indian listed entity is an indirect subsidiary of the overseas parent.
Indirect holding can have complex structures involving one or more subsidiaries of the parent company. Understanding this holding needs you to understand the below terminologies.
- Ultimate Holding Company
- Intermediate Holding Company
- Immediate Holding Company
Let us discuss each of these in details with examples.
Ultimate Holding Company
Academic definition: Ultimate Holding Company is the parent company and is not a subsidiary of any other entity, i.e. No other entity is holding this company. (Reference: Corporate Finance Institute)
In the indirect mode of holding, the overseas parent does not directly have major stakes in the Indian listed entity. The overseas parent (referred to as Ultimate Holding Company) holds it indirectly through its other subsidiary/subsidiaries. If it is not clear, please be with me. It will be clear in a while when I discuss with examples.
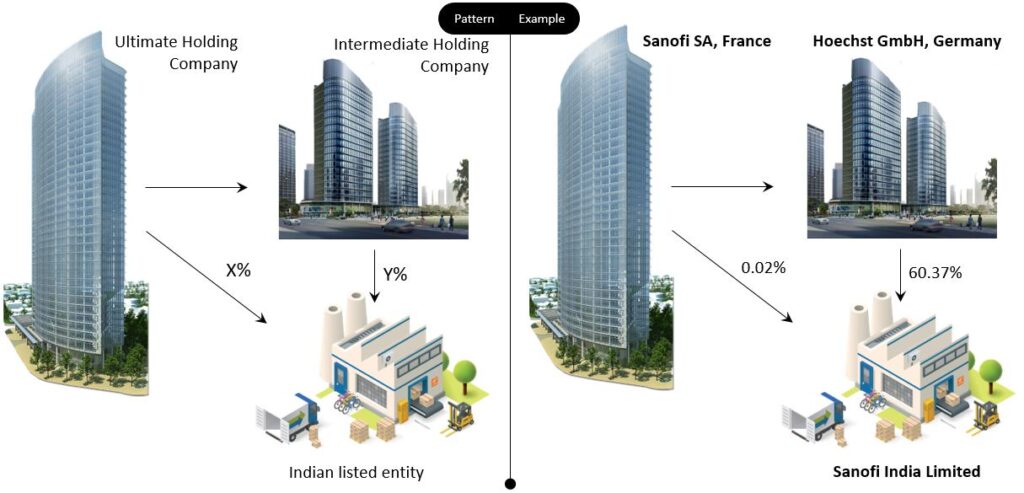
Intermediate Holding Company
Academic definition: Intermediate holding company is both, (1) A holding company of another entity and (2) A subsidiary of a larger corporation, with could either be the Ultimate Holding Company or another Intermediate Holding Company.
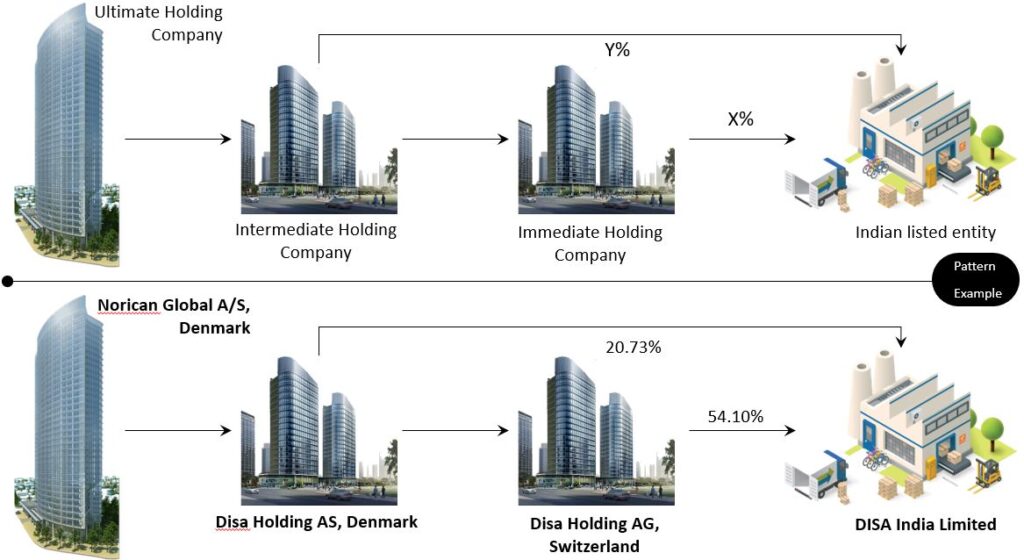
The Intermediate Holding Company, a subsidiary of the ultimate holding company holds the Indian listed entity. Below is the pattern and example.
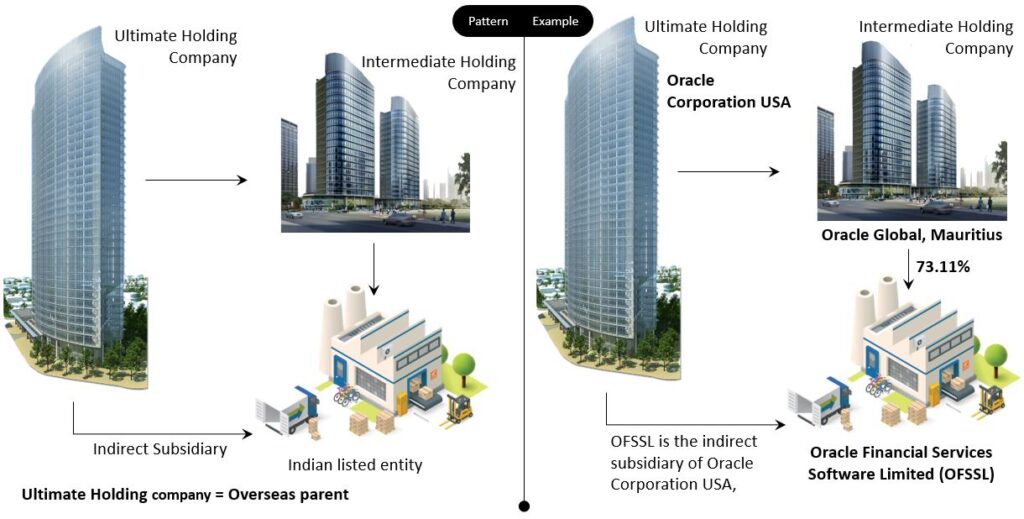
As told earlier, indirect holdings can sometimes be quite complex. Let us discuss a few complex structures.
1. Multiple intermediate holding companies could have stakes in the Indian listed entity. In simpler terms, multiple subsidiaries of the Ultimate Holding Company hold the Indian listed entity. Below is the pattern and example.
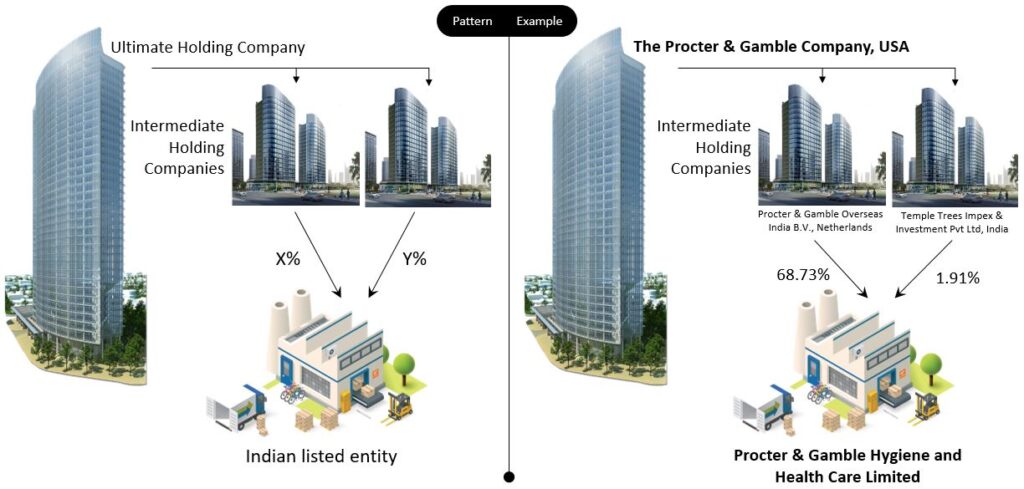
A bit complex example with 4 Intermediate Holding Companies.
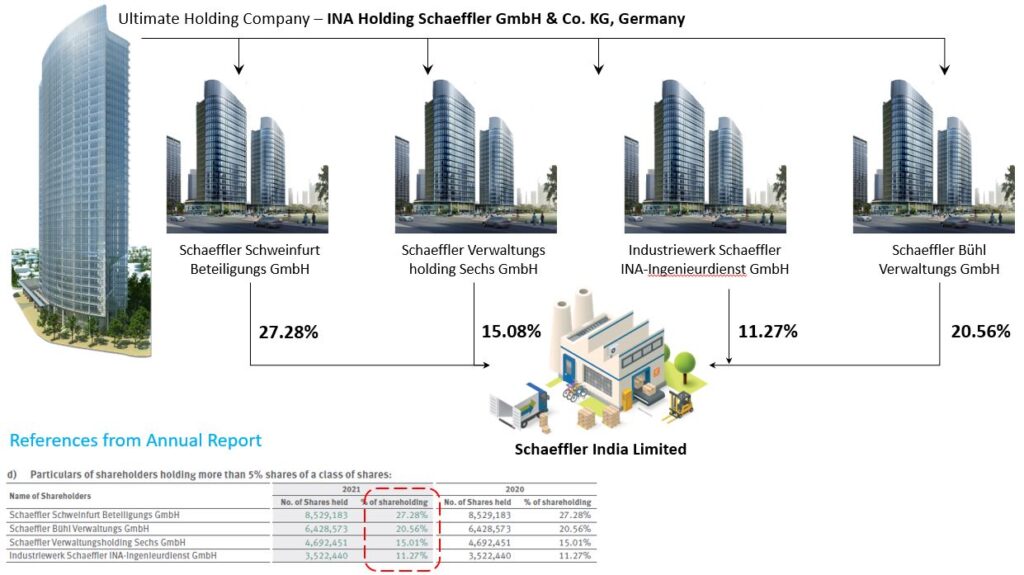
2. At times apart from the intermediate holding company, the Ultimate Holding Company may also have some stakes in the Indian listed entity. Below is the pattern and example.
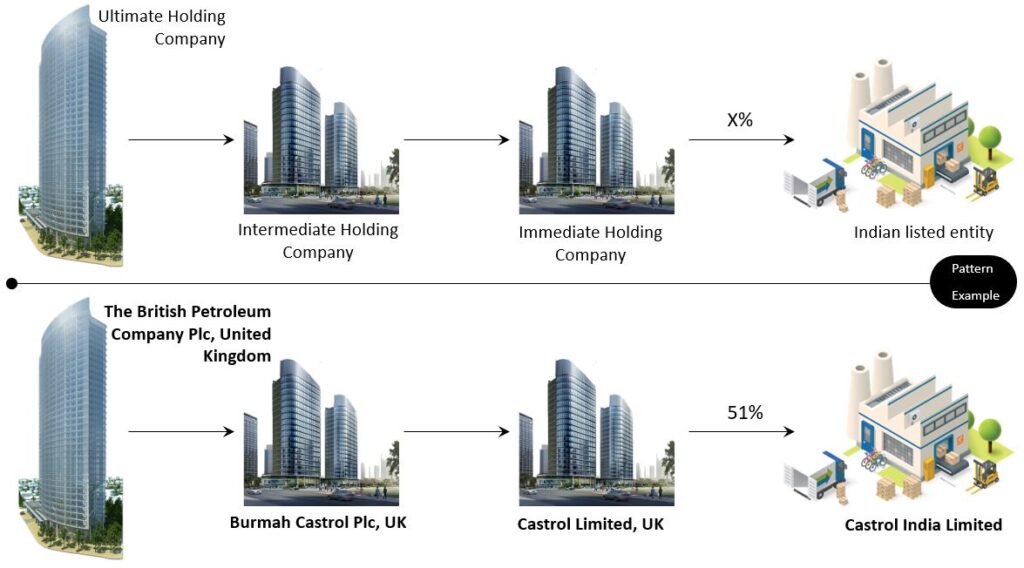
Immediate Holding Company
This company holds the Indian listed entity. The Immediate Holding Company is:
- Not held by the Ultimate Holding Company.
- A subsidiary of an intermediate holding company
In simpler terms, this company holds the Indian listed entity, while it is a subsidiary of the Intermediate Holding Company. Below is the pattern and example.
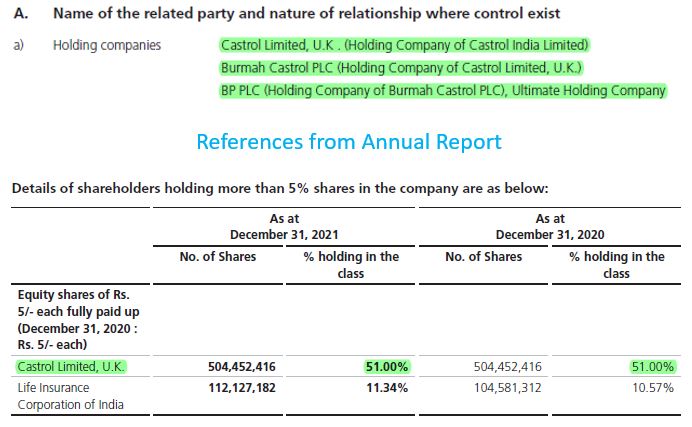
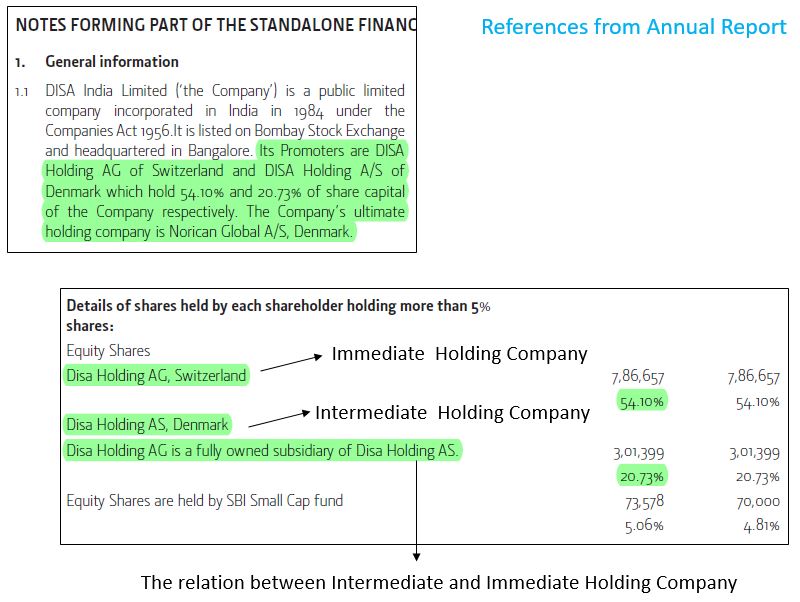
Reference of the above details from the annual report.
At a complex level, the intermediate holding company may also have some stakes in the Indian listed entity. Below is the pattern and example.
Reference of the above details from the annual report.
Direct Vs. Fellow Subsidiary
Let us first understand the definition of a subsidiary.
A subsidiary is a business entity or corporation fully owned or partially controlled by another company, termed as the parent or holding company. Ownership is determined by the percentage of shares held by the parent company, and that ownership stake must be at least 51%. (Reference: Corporate Finance Institute)
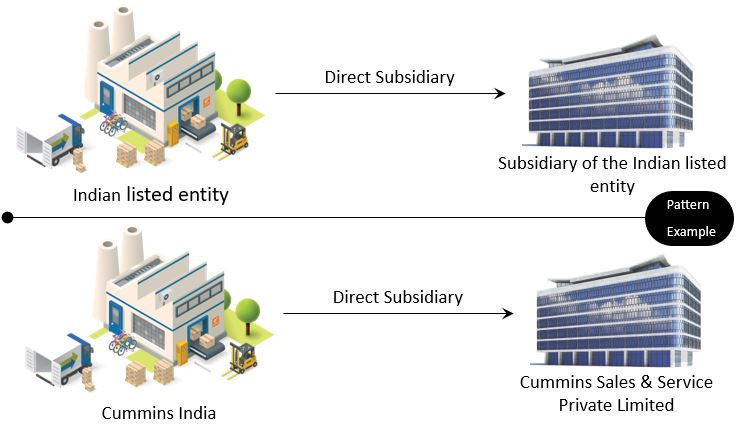
Direct Subsidiary
Let us start with the basic building block. The listed Indian entity could have some subsidiaries with 51% or above stakes. To avoid ambiguity the term “direct subsidiary” is used.
Fellow Subsidiary
To the above basic building block bring in the below entities:
- Ultimate Holding Company
- Intermediate Holding Company and/or Immediate Holding Company
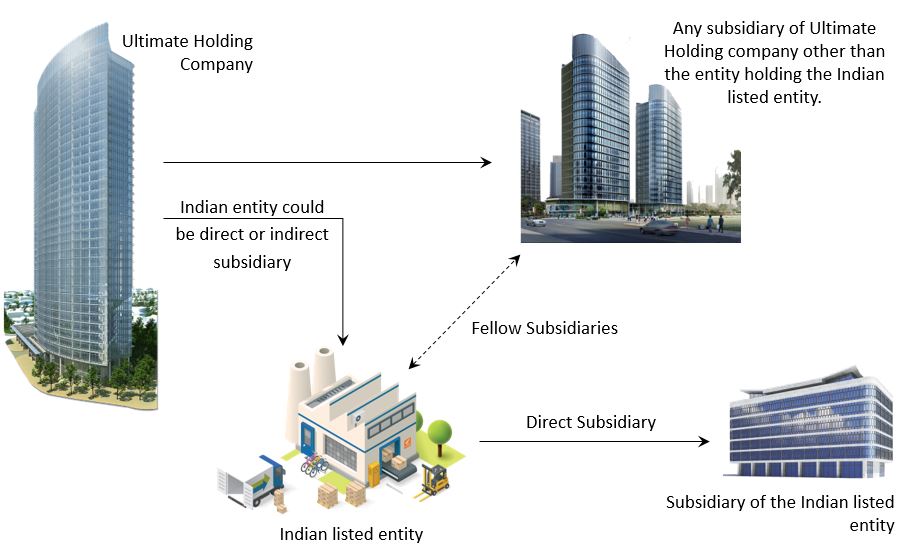
Thus all direct and indirect subsidiaries of the Ultimate Holding Company are fellow subsidiaries to the Indian listed entity with the below exception.
The subsidiary of the Ultimate Holding Company should not be the holding company of the Indian listed entity. Because it then becomes the intermediate or immediate holding company for the Indian listed entity and not a fellow subsidiary. An example below.
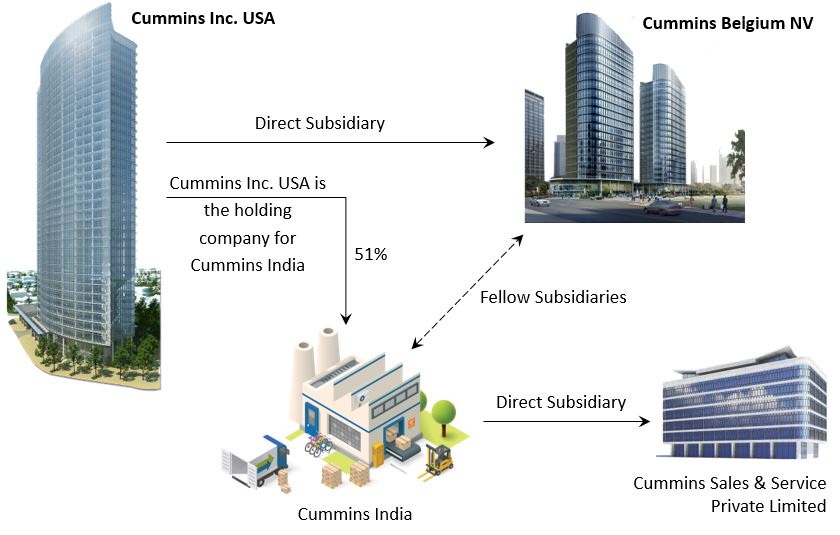
All these details are well covered in the annual report. You only need to search with the right keywords. In this case, the keywords are “Holding company”, “Fellow Subsidiary” and “Subsidiary”. You get all the information in the above image.
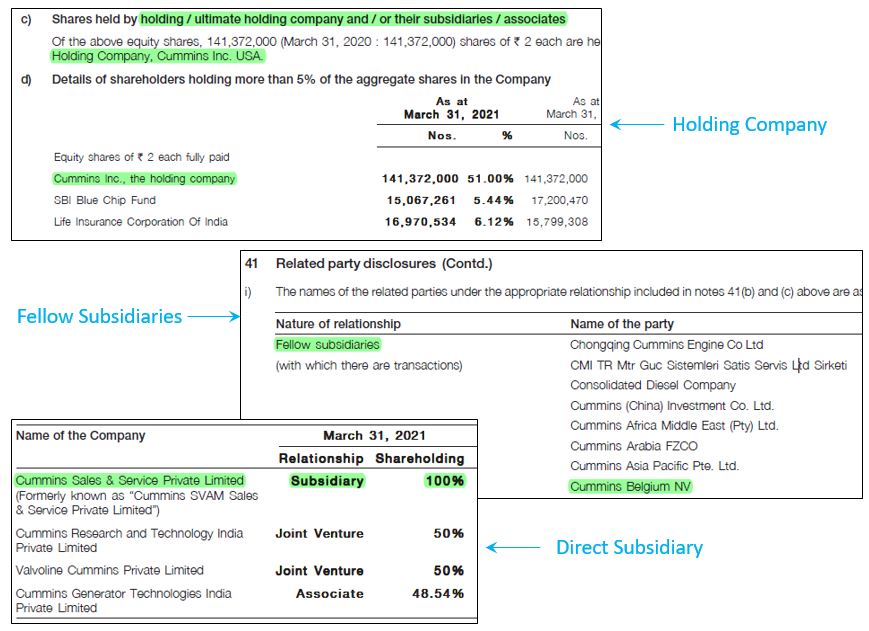
Importance of this information
The very purpose of covering this aspect is to analyse the related party transactions. The Indian listed entity can have related party transactions with any of these entities
- Ultimate Holding Company
- Intermediate Holding Company
- Immediate Holding Company
- Fellow subsidiaries
Analysis of these related party transactions gives insight into corporate governance. Which is covered in the next blog.
Hope you found this blog useful. Do share my blogs with your friends, peers and fellow investors.

